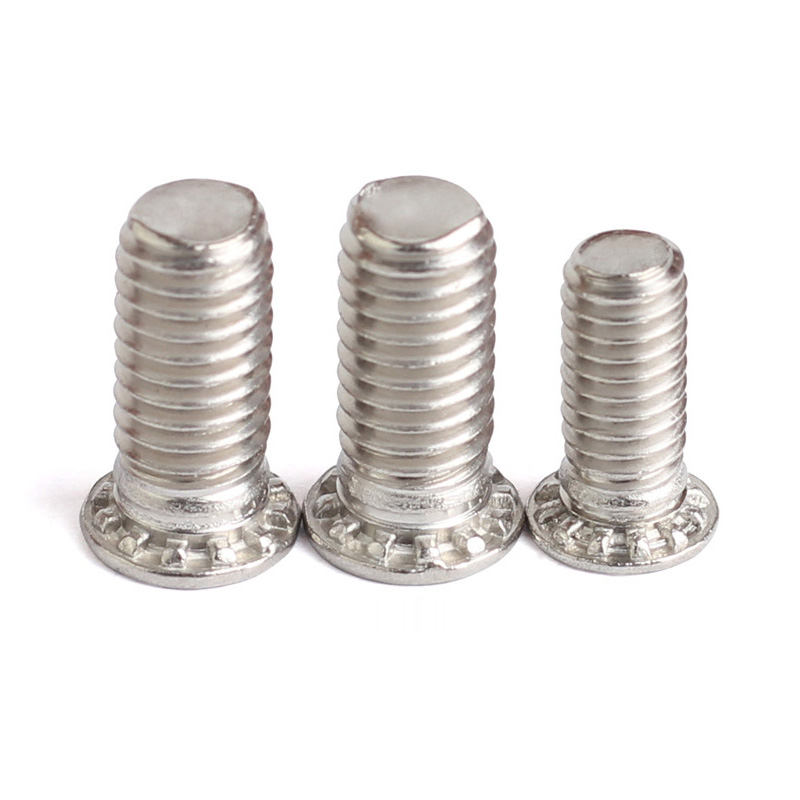
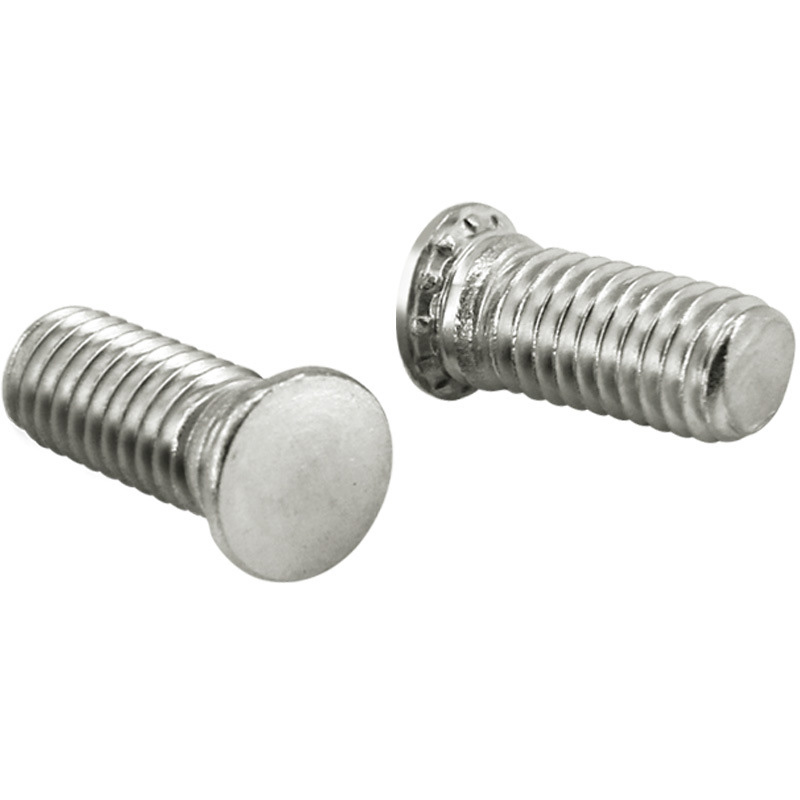
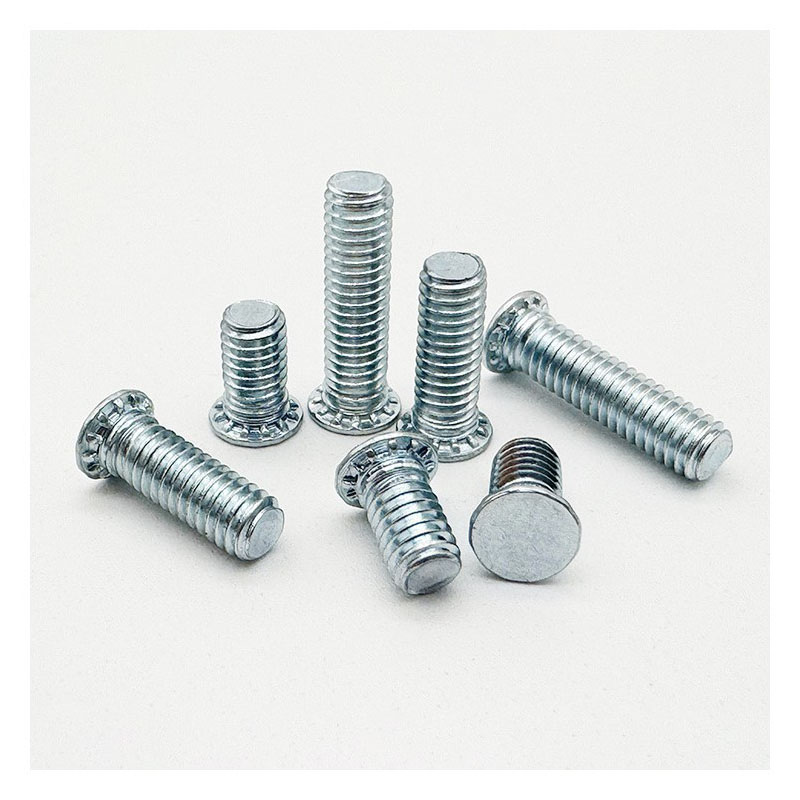
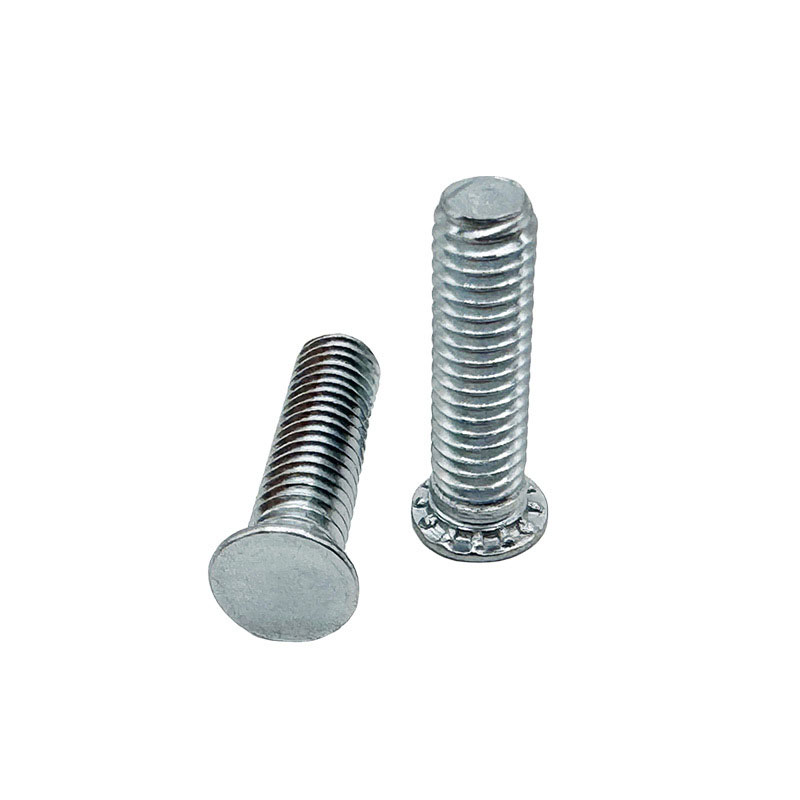
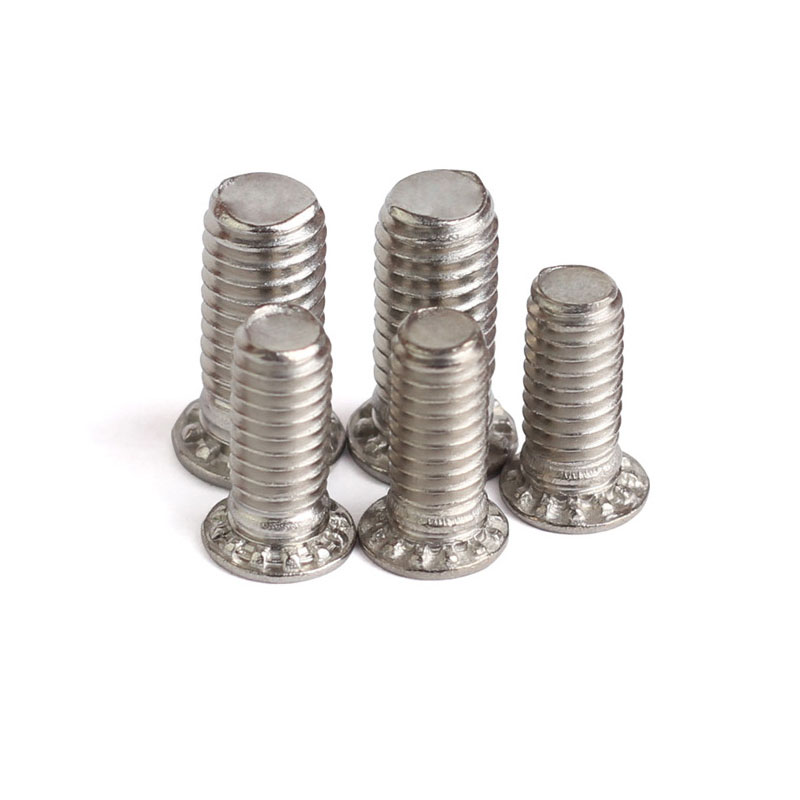
Carbon Steel Concealed Head Threaded Studs
Send Inquiry
About those carbon steel concealed head threaded studs made of carbon steel.Well, actually, carbon steel ones are common, but hide headed riveted screws are also frequently made from corrosion-resistant stainless steels (like the austenitic types, you know). These screws have to follow specific standards like ASTM A193, or sometimes NASM25027 and MS90373.
These standards basically spell out the rules: what's in the screws (their chemical mix), how strong they need to be (like tensile and yield strength), and what tests they must pass. The whole point is to make sure the concealed head threaded studs work properly and you can track where they came from and how they were produced. Following these standards just keeps the quality consistent.
Advantage
The biggest advantage of carbon steel concealed head threaded studs is that they do not require special maintenanceThat's mostly because they're pretty rust-resistant on their own. Honestly, just giving them a look-over every now and then to check for any rust (which is rare if you picked the right grade for the job) or if they got banged up is usually enough.
Try to keep these concealed head threaded studs from touching really reactive metals, like certain other steels. If they do touch, that can kick off galvanic corrosion, that special kind of rust that happens when different metals are in contact.
These hide headed riveted screws just last ages. You can pretty much set them and forget them,hardly any regular upkeep needed.
Package
We pack carbon steel concealed head threaded studs securely for export. Standard options include sturdy cardboard cartons with inner plastic bags or bulk boxes with dividers. We ensure packaging prevents movement, abrasion, and moisture ingress during transit, protecting the precise head geometry and threads crucial for proper riveting and performance
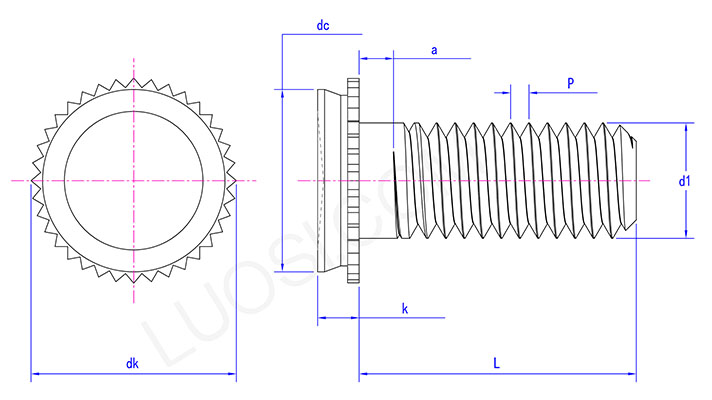
Product parameters
| Mon | M3 | M4 | M5 |
| P | 0.5 | 0.7 | 0.8 |
| k max | 1.04 | 1.04 | 1.04 |
| dc max | 4.35 | 7.35 | 7.9 |
| dk max | 5.46 | 8.58 | 9.14 |
| dk min | 4.96 | 8.08 | 8.64 |
| d1 | M3 | M4 | M5 |
| a max | 1.6 | 1.6 | 1.6 |















