Aerospace Validated Aircraft Steel Wire Rope
Send Inquiry
Aerospace Validated Aircraft Steel Wire Rope is built for critical aerospace and aviation uses where reliability matters most. It’s used to secure aircraft control surfaces like flaps and ailerons, support cargo lifting systems in cargo planes, and fix emergency escape slide components in passenger jets.
It also works for ground support equipment—like towing aircraft or lifting engine parts during maintenance. Outside aviation, it fits heavy-duty industrial jobs that need high strength and anti-fatigue performance, such as lifting precision machinery or stabilizing large structures. No extra frills, just steady performance for tasks that can’t afford to fail.
Product Packaging
Aerospace Validated Aircraft Steel Wire Rope is packaged to avoid damage during transit and storage. Small rolls are wrapped in waterproof plastic film, then put into thick cardboard tubes to keep the rope from bending or tangling.
Bulk orders are coiled neatly and placed in wooden crates lined with soft padding—this stops the rope from rubbing against hard surfaces and getting scratched. Every package is labeled with basic info like length, diameter and batch number, so you can check what you’ve got at a glance. We don’t add any extra packaging layers, just what’s needed to make sure the rope arrives in good shape.
Q&A Session
What materials are used to make Aerospace Validated Aircraft Steel Wire Rope?
A: This type of aviation steel wire rope is mainly made of high-purity carbon steel or stainless steel. The reason for choosing these two materials is that they have sufficient tensile strength and fatigue resistance, which are precisely the qualities most highly valued in aviation applications.
Specifically, the impurities in carbon steel are strictly controlled to ensure stable performance. The types of stainless steel are designed to withstand environments prone to rust, such as those used in marine aviation equipment.
During the production process, each batch of materials must undergo testing and must meet the set standards of the aviation industry. Only in this way can the ropes produced be reliable and usable under the demanding conditions of actual flights.
|
Diameter mm |
Nominal tensile strength |
Minimun breaking loa |
Approximate weight kg/100m |
|
| Nominal diameter | Allowed tolerance | |||
|
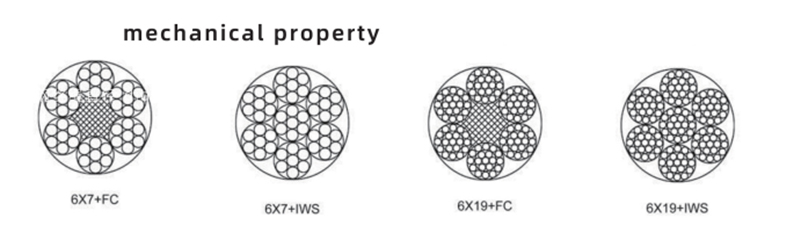
6x7+FC |
||||
| 1.8 | +100 | 1960 | 2.3 | 1.40 |
| 2.15 |
+80 |
1960 |
3.3 | 2.00 |
| 2.5 | 4.5 | 2.70 | ||
| 3.05 |
1870 |
6.3 | 4.00 | |
| 3.6 | 8.7 | 5.50 | ||
| 4.1 |
+70 |
1770 |
10.4 | 7.00 |
| 4.5 | 12.8 | 8.70 | ||
| 5.4 | 1670 | 17.5 | 12.50 | |
|
6x7+IWS |
||||
| 1.8 | +100 |
1870 |
2.5 | 1.50 |
| 2.15 |
+80 |
3.6 | 2.20 | |
| 2.5 | 5.0 | 3.00 | ||
| 3.05 | 7.3 | 4.40 | ||
| 3.6 | 10.1 | 6.20 | ||
| 4.5 |
+70 |
1770 | 15.0 | 9.60 |
| 5.4 | 1670 | 20.4 | 13.80 | |
|
6x19+FC |
||||
| 3 |
+80 |
2060 | 6.3 | 3.80 |
| 3.3 |
1770 |
6.5 | 4.50 | |
| 3.6 | 7.8 | 5.40 | ||
| 4.2 |
+30 |
10.6 | 7.40 | |
| 4.8 | 12.9 | 9.00 | ||
| 5.1 | 15.6 | 10.90 | ||
| 6.2 | 1670 | 20.3 | 15.00 | |
|
6x19+IWS |
||||
| 3 |
+80 |
2060 | 7.3 | 4.20 |
| 3.2 | 2160 | 8.9 | 4.30 | |
| 3.6 |
1770 |
9.1 | 6.00 | |
| 4.2 |
+70 |
12.3 | 8.20 | |
| 5.1 | 18.2 | 12.10 | ||
| 6 |
1670 |
23.7 | 16.70 | |
| 7.5 |
+50 |
37.1 | 26.00 | |
| 8.25 | 44.9 | 32.00 | ||
| 9 | 53.4 | 37.60 | ||
| 9.75 | 62.6 | 44.10 | ||














