Weld Studs For Plastics
Send Inquiry
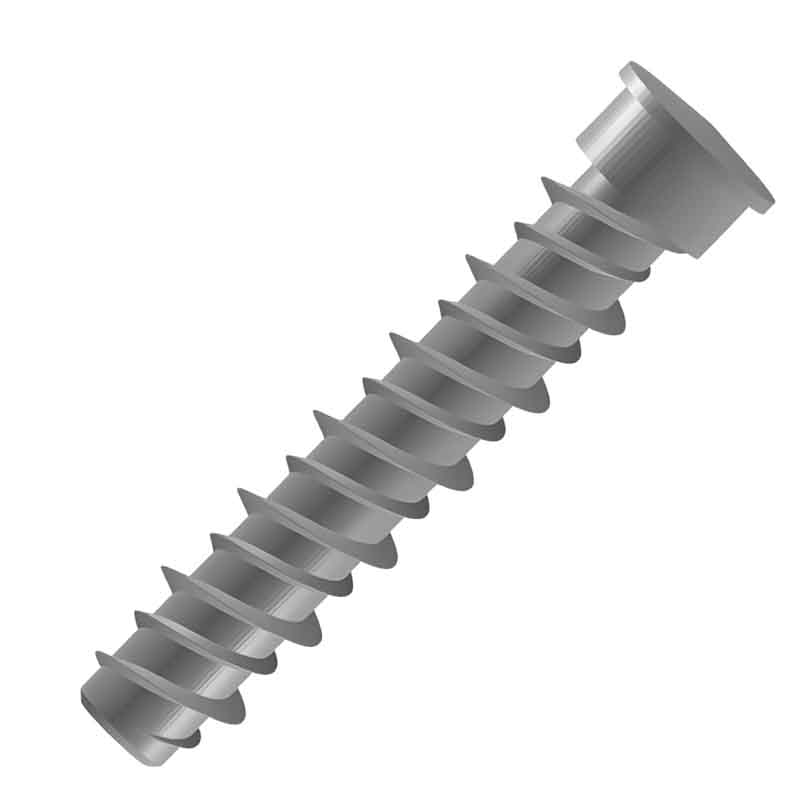
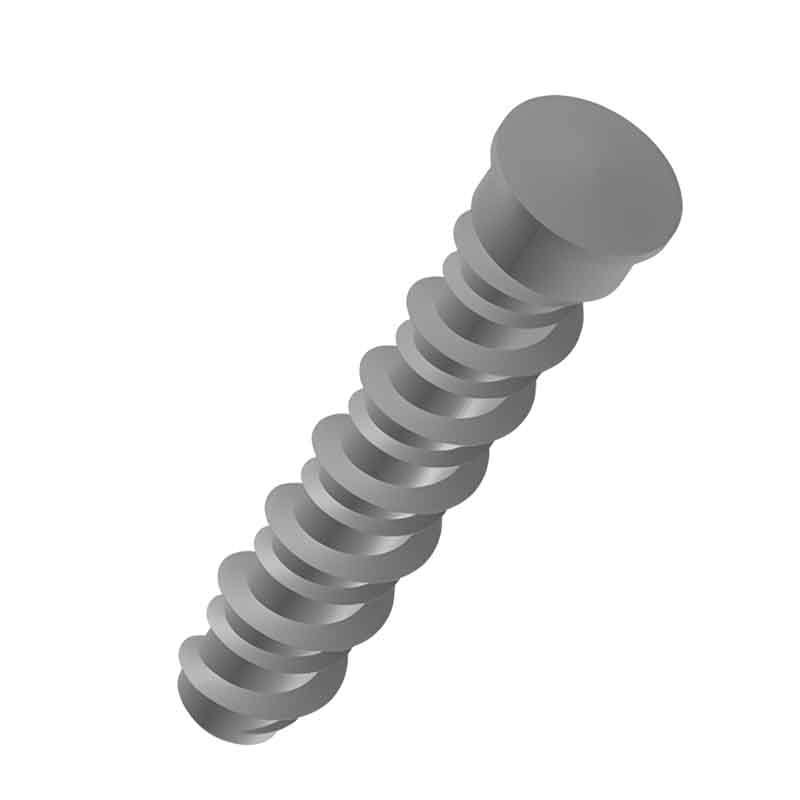
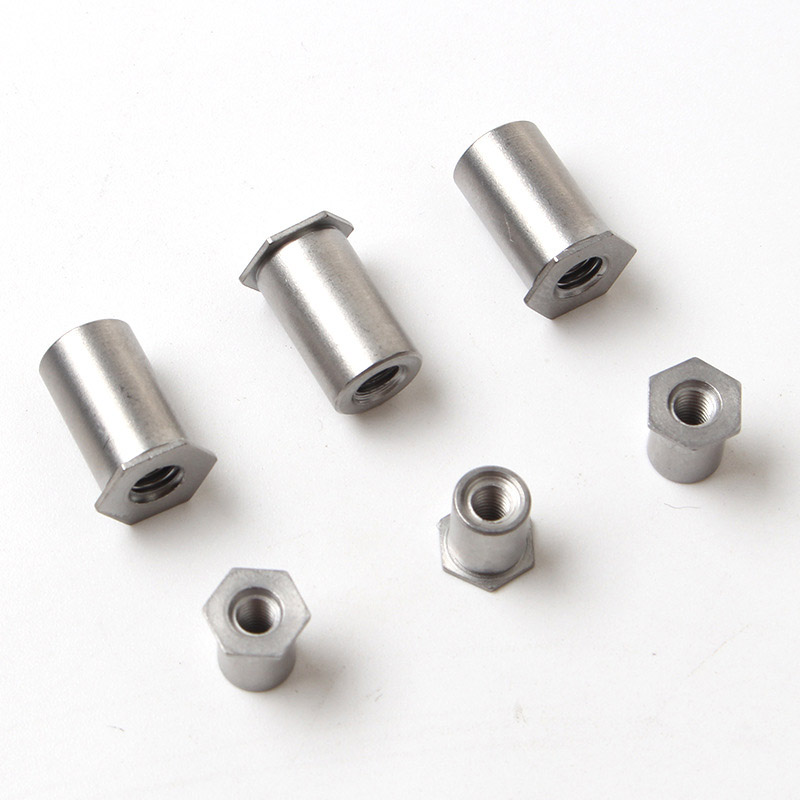
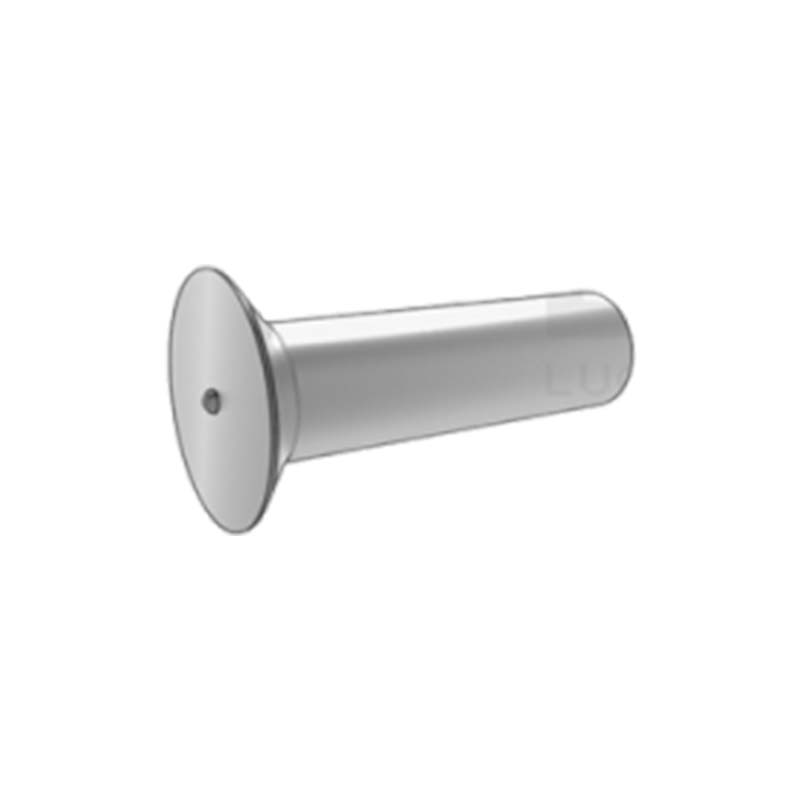
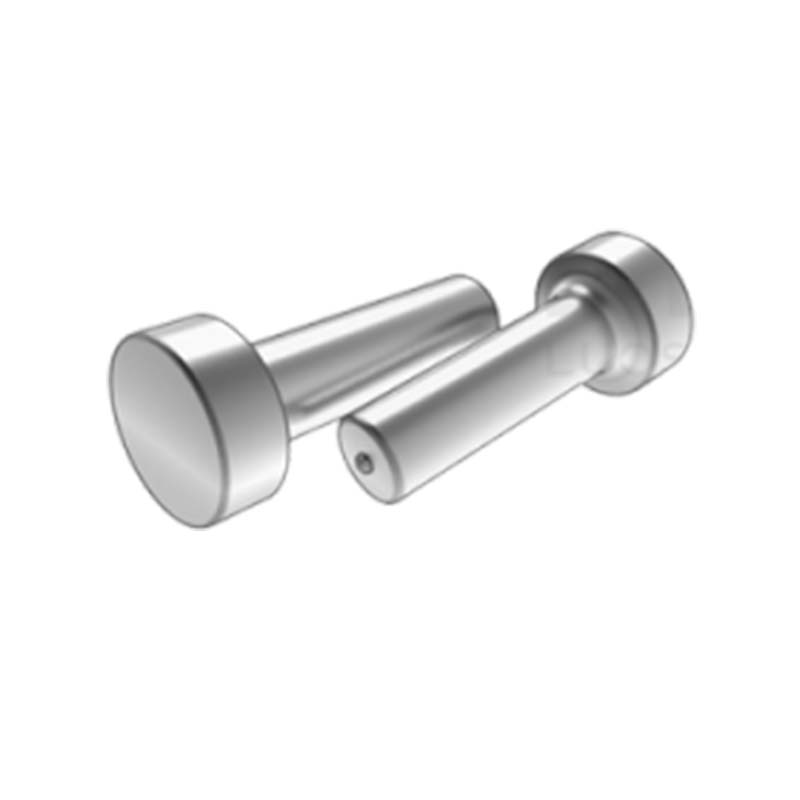
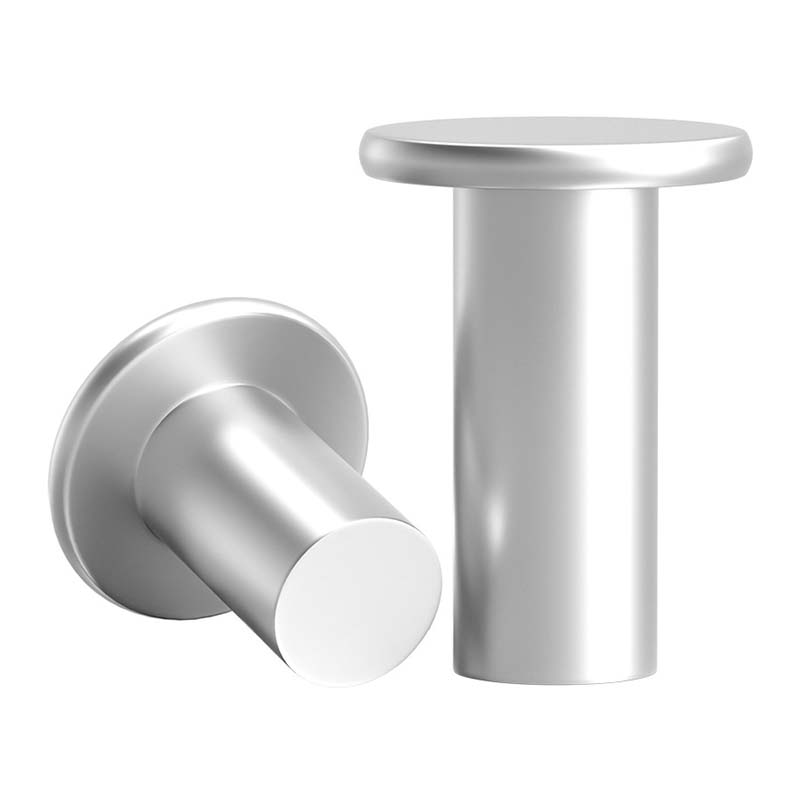
The weld studs for plastics look like small columns. One end has threads that can be used to tighten nuts, while the other end is for welding onto the plastic. They can be adapted to different thicknesses of plastic sheets or parts.
Product features and applications
These weld studs are connected by melting thermoplastic. A special tool is used to heat the tip of the stud, which is then pressed into the plastic surface and cooled. The plastic flows along the groove, securely locking it in place. Instantly threaded anchoring can be formed in the panel or casing.
Weld studs for plastics can be directly welded to compatible materials (such as PP, ABS or PVC). No metal inserts are required. Melt the screw base into the plastic, and after it solidifies, it can be used for bonding. It is more durable than glue and can be disassembled and reassembled repeatedly.
The design of the welding ends of weld studs is very meticulous. The shape and surface treatment are conducive to quick integration with plastics, and during the welding process, they can ensure that the plastics are heated evenly, forming a firm connection. The thread of the screw stud is of high precision. When tightening the nut, it moves smoothly without any jamming or thread breakage.
In the automotive interior manufacturing industry, weld studs for plastics have a wide range of applications.Just like the plastic frame of a car seat, small components such as seat adjustment buttons and seat belt clips can be installed by welding them to the frame first and then screwing them onto the bolts. This way, no matter how the seat is adjusted or the seat belt is pulled during emergency braking, these components will not easily fall off, ensuring the stability of the interior and safety components.
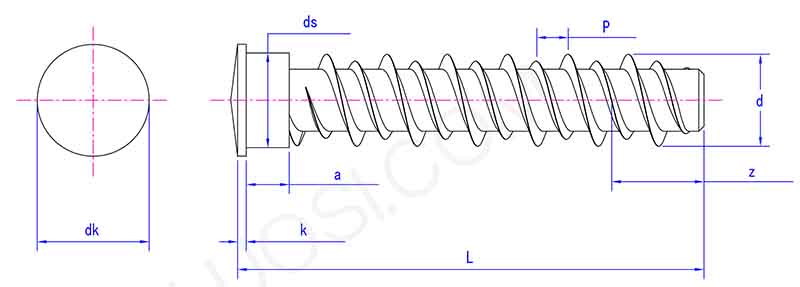
Product parameters
|
Mon |
NST5 |
|
P |
1.6 |
|
dk max |
6.3 |
|
dk min |
5.7 |
|
k max |
0.85 |
|
k min |
0.55 |
|
a max |
3 |
|
ds max |
5.1 |
|
ds min |
4.85 |
|
z max |
3.6 |