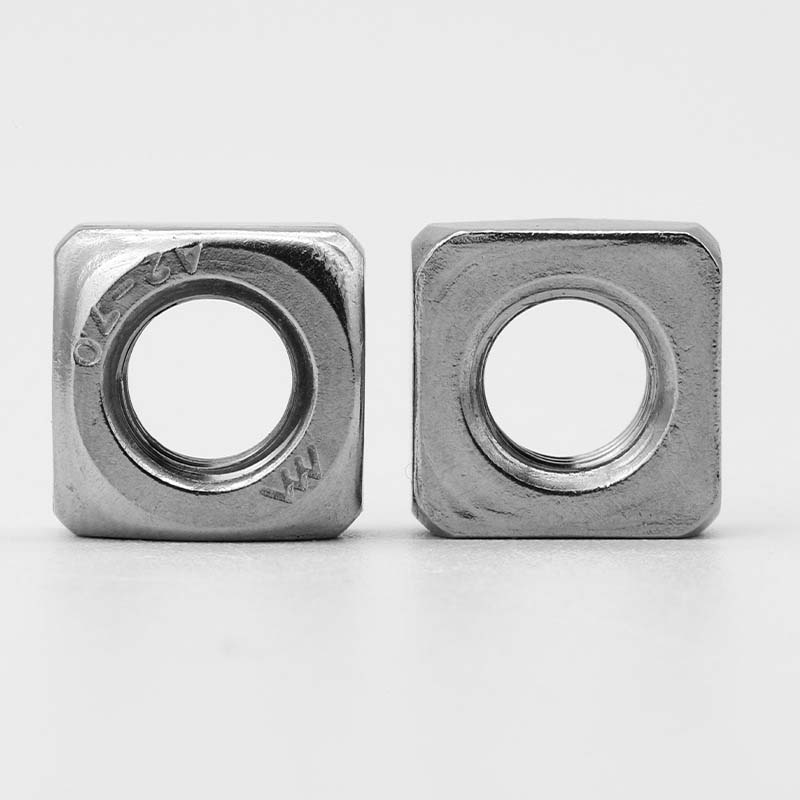
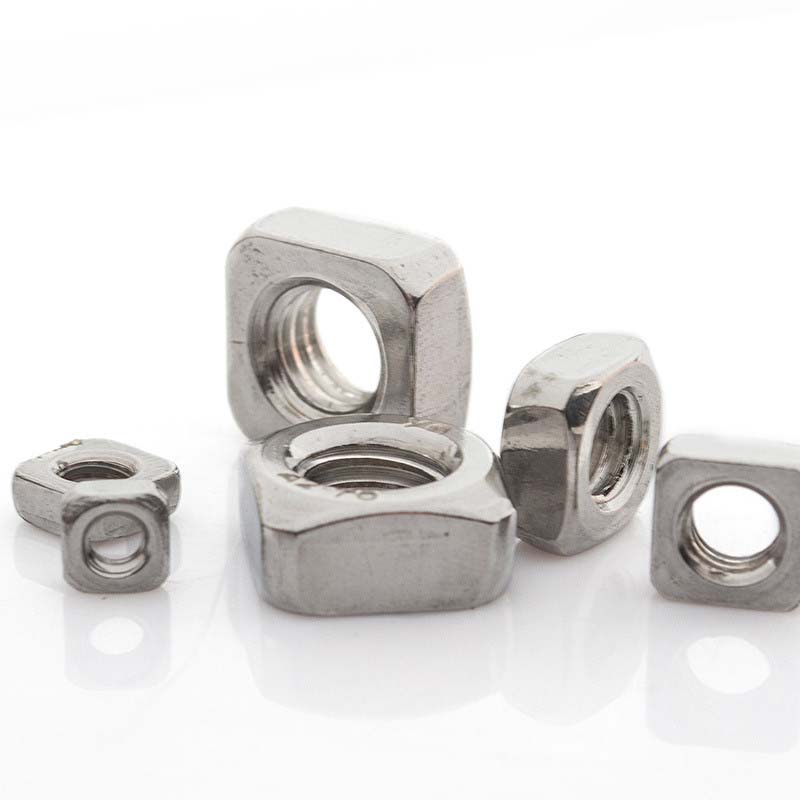
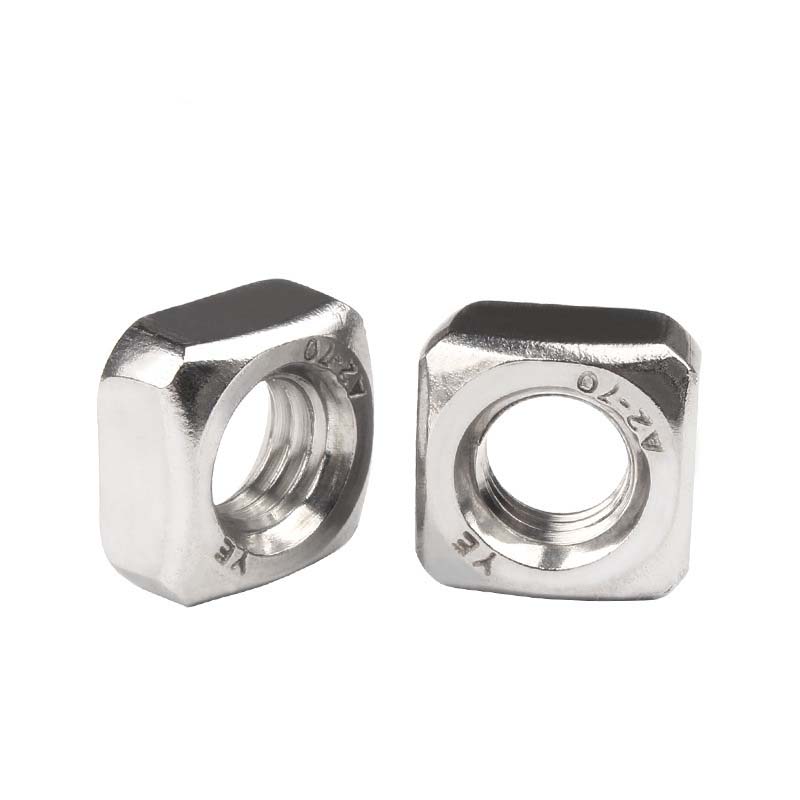
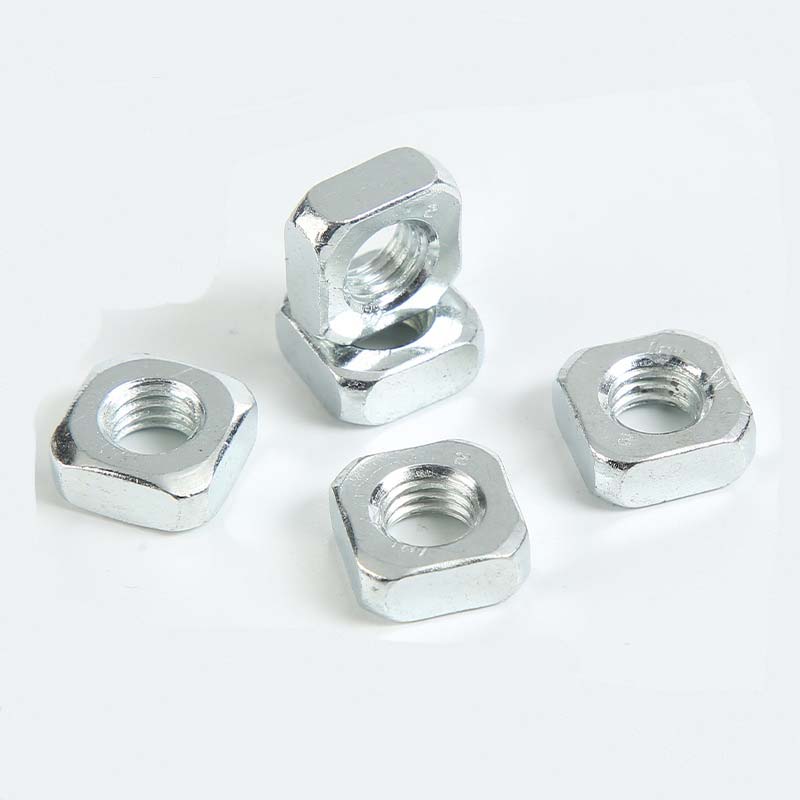
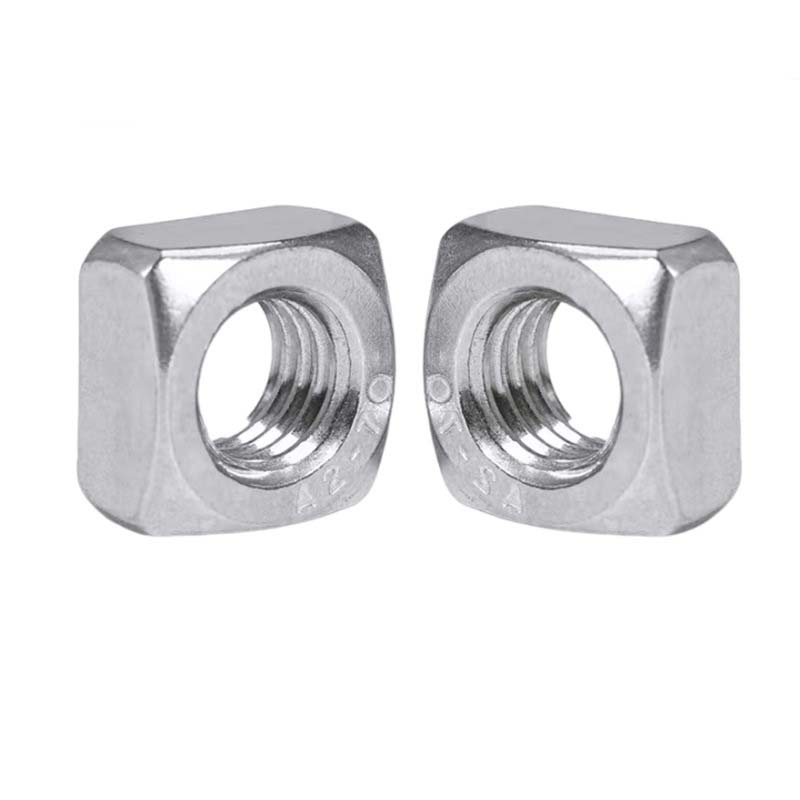
Single Chamfered Square Nuts
Send Inquiry
To make single chamfered square nuts last longer and resist rust better, they get different surface treatments. Common ones include zinc plating,usually yellow or clear chromated,which gives basic rust protection. For tough conditions, hot-dip galvanizing puts on a thick, strong zinc coating. Plain (unfinished) ones are used indoors, while black oxide gives some rust resistance and cuts down on glare. Electroplated cadmium (not used as much these days) or special coatings like Geomet® are also options for specific needs.
Mon
3/8
7/16
1/2
5/8
3/4
7/8
1
1-1/8
1-1/4
1-3/8
1-1/2
P
16
14
13
11
10
9
8
7
7
6
6
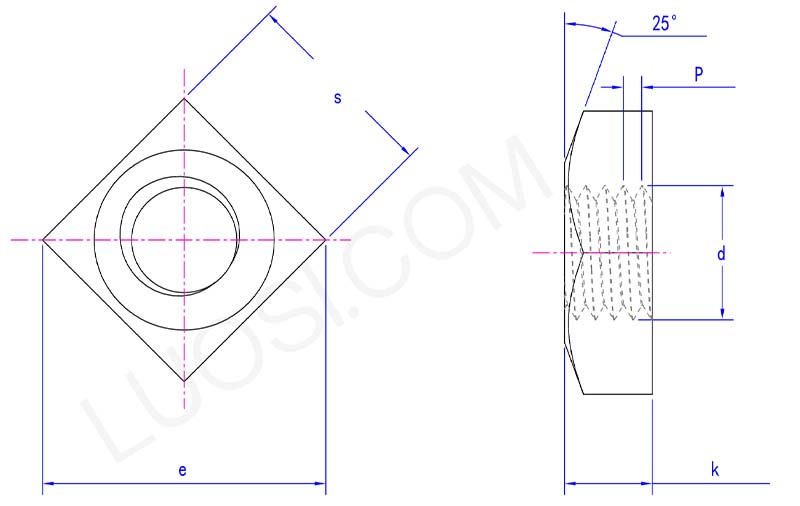
s max
0.625
0.750
0.813
1.000
1.125
1.313
1.500
1.688
1.875
2.063
2.250
s min
0606
0.728
0.788
0.969
1.088
1.269
1.450
1.631
1.812
1.994
2.175
e max
0.884
1.061
1.149
1.414
1.591
1.856
2.121
2.386
2.652
2.917
3.182
e min
0.832
1.000
1.082
1.330
1.494
1.742
1.991
2.239
2.489
2.738
2.986
k max
0.346
0.394
0.458
0.569
0.680
0.792
0.903
1.030
1.126
1.237
1.348
k min
0.310
0.356
0.418
0.525
0.632
0.740
0.847
0.970
1.062
1.169
1.276
Follow standards
Single chamfered square nuts follow common standards like ASME B18.2.2, DIN 557, or ISO 4034. That way, they can be swapped out easily and work as they should.
Main sizes include things like the thread size,say M12 or 1/2 inch,the width across the square's flats, height (how thick they are), and the exact thread pitch and class, like M12x1.75 or Class 8.
The square's size lines up with the thread size, so they fit with the right square holes and the tools or ways you put them together.
Corrosion protection options
To enhance the strength and extend the service life of single chamfered square nuts, we offer a variety of coatings. Common coatings include hot-dip galvanizing (HDG), zinc plating, or mechanical galvanizing in accordance with ASTM A153. We select and apply coatings that are compatible with these high-strength square nuts, ensuring they are immune to hydrogen embrittlement. They provide rust resistance without compromising their primary strength.















