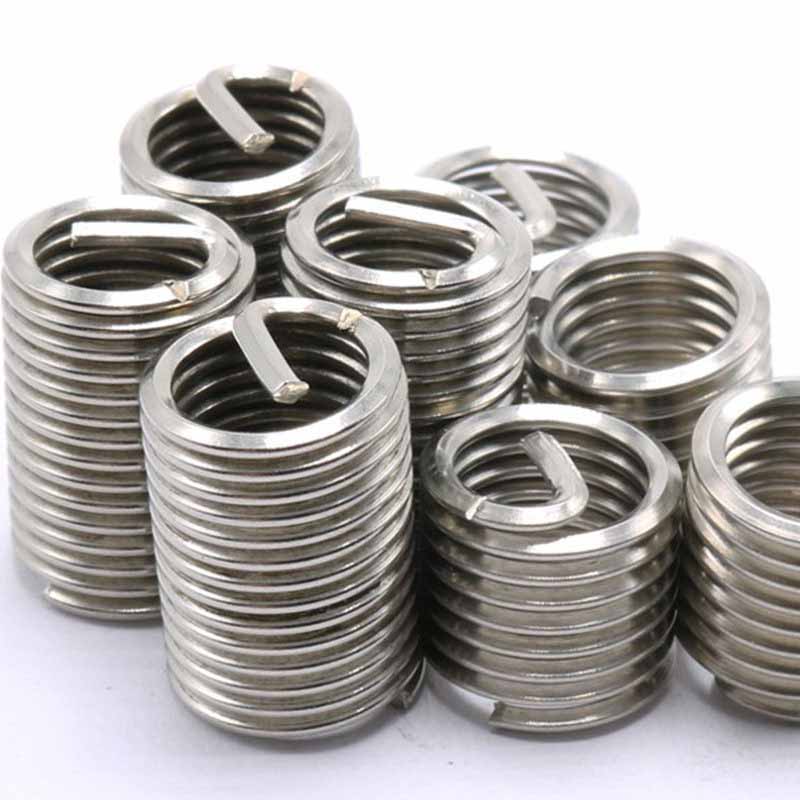
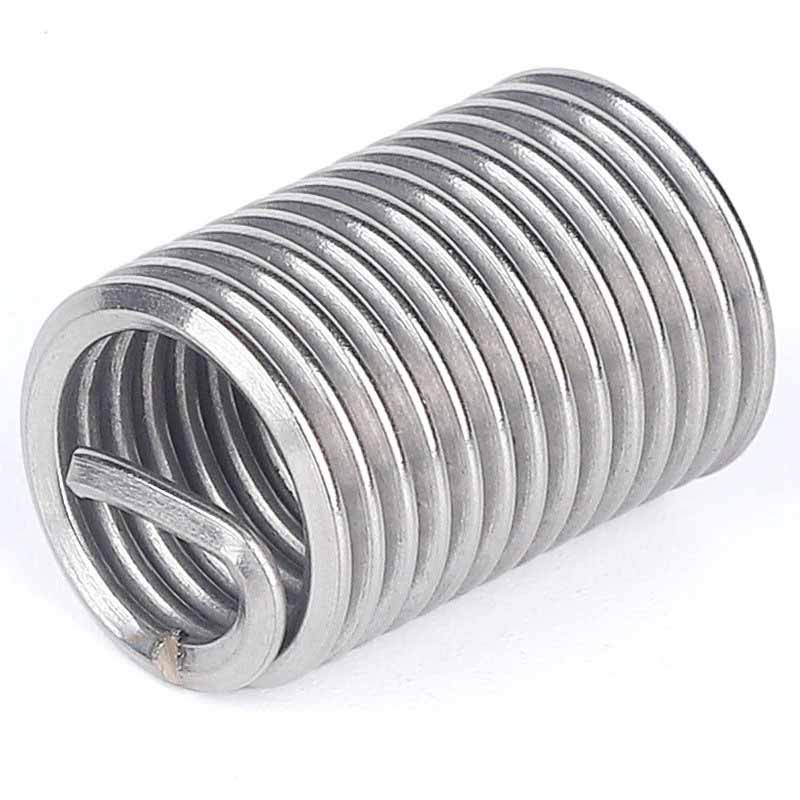
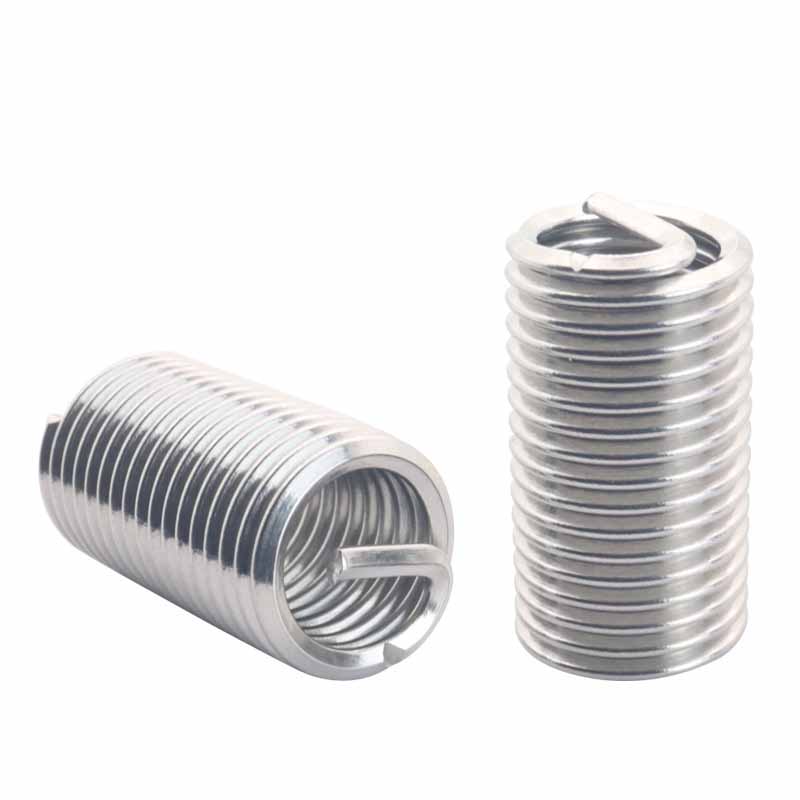
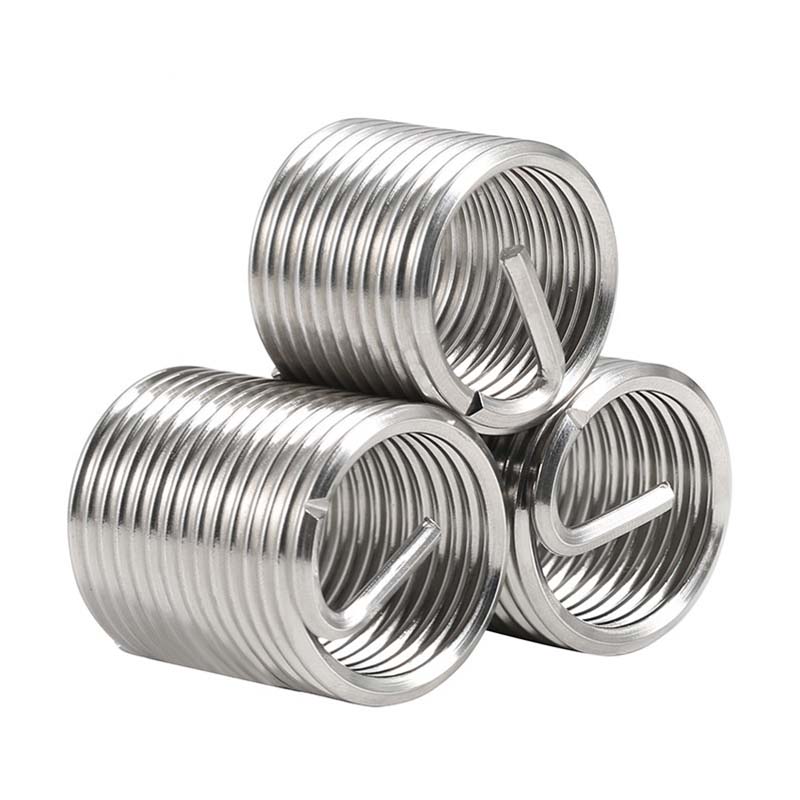
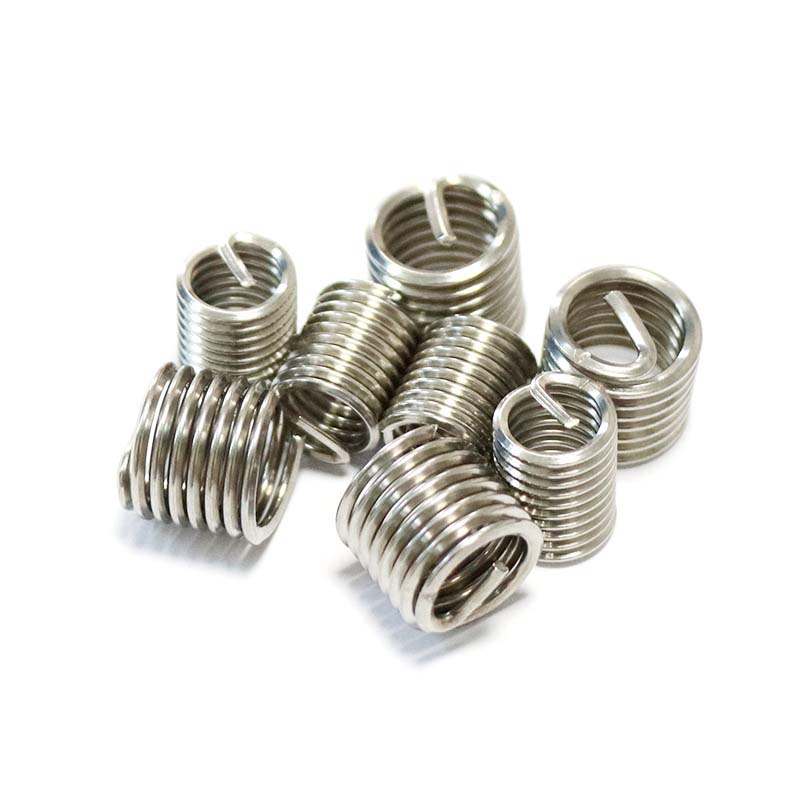
Stainless Steel Wire Thread Insert
Send Inquiry
The material of choice for making Stainless Steel Wire Thread Insert is phosphor bronze (the stuff covered in standards like ASTM B159 and ASTM F468). It has good anti-rust and anti-corrosion properties and can be used in seawater and chemical environments. The copper alloy is light and high, with a smooth surface, and is very smooth to screw in and out. It can be used for a long time and has good wear resistance, making it very popular in the market. Phosphor bronze screw plugs aren't magnetic, and they work reliably in places like marine gear, hydraulic systems, and chemical plants. They make sturdy threads that handle tightening and loosening without getting messed up easily.
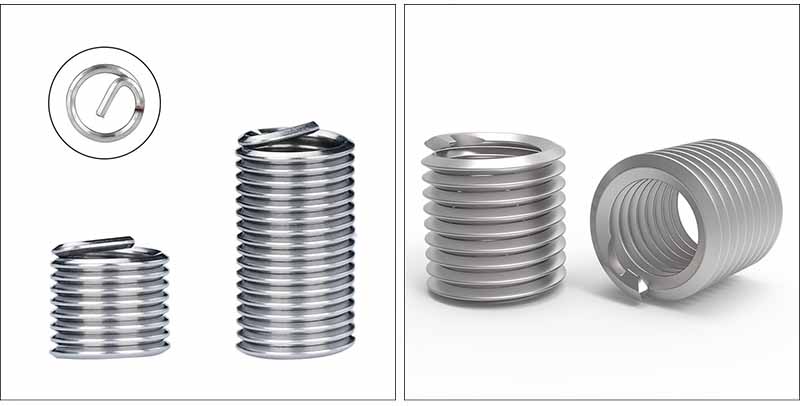

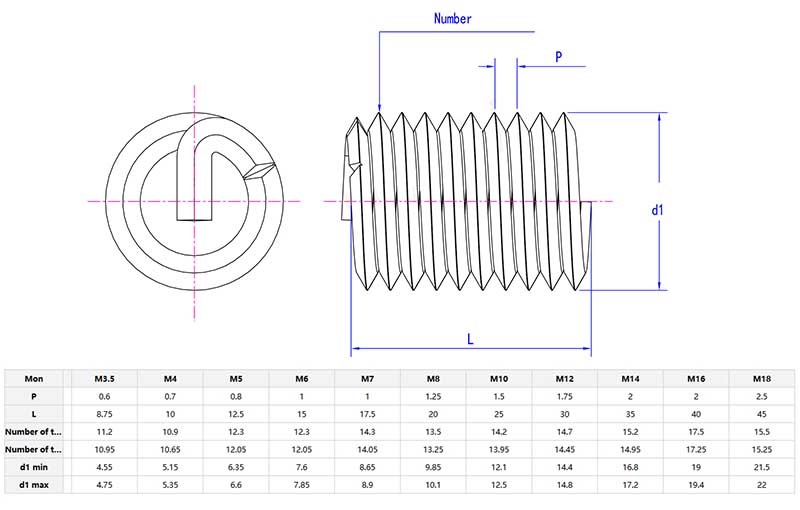
Product details and parameters
Stainless steel screw plugs – usually the 18-8 type, like 304 or 305 covered in ASTM F138 – are the go-to choice when you need good strength and solid corrosion resistance. They handle heavy loads and heat pretty well. It is rust-resistant and corrosion-resistant that can be used in high-demand places such as food processing plants, medical equipment, aerospace equipment and outdoor equipment. They last well and don't fail easily in these tough conditions.
FAQ
Q: What materials are Stainless Steel Wire Thread Insert typically made from, and how do I choose the right one for corrosion resistance?
A: Common screw plug materials include:
18-8 (like 304) stainless steel: Used for general jobs.
316 stainless steel: Handles saltwater and chemicals better.
Phosphor bronze: Good where sparks could be dangerous.
High-temp alloys (like Inconel): For really hot spots.
Which one you grab depends on where you'll use it. For fighting rust/corrosion, pick a material that matches or beats the base material's resistance. A 316 Stainless Steel Wire Thread Insert is often a common pick for harsh marine or chemical spots to avoid problems caused by different metals reacting.













