Wheel Hub Bolt
Send Inquiry
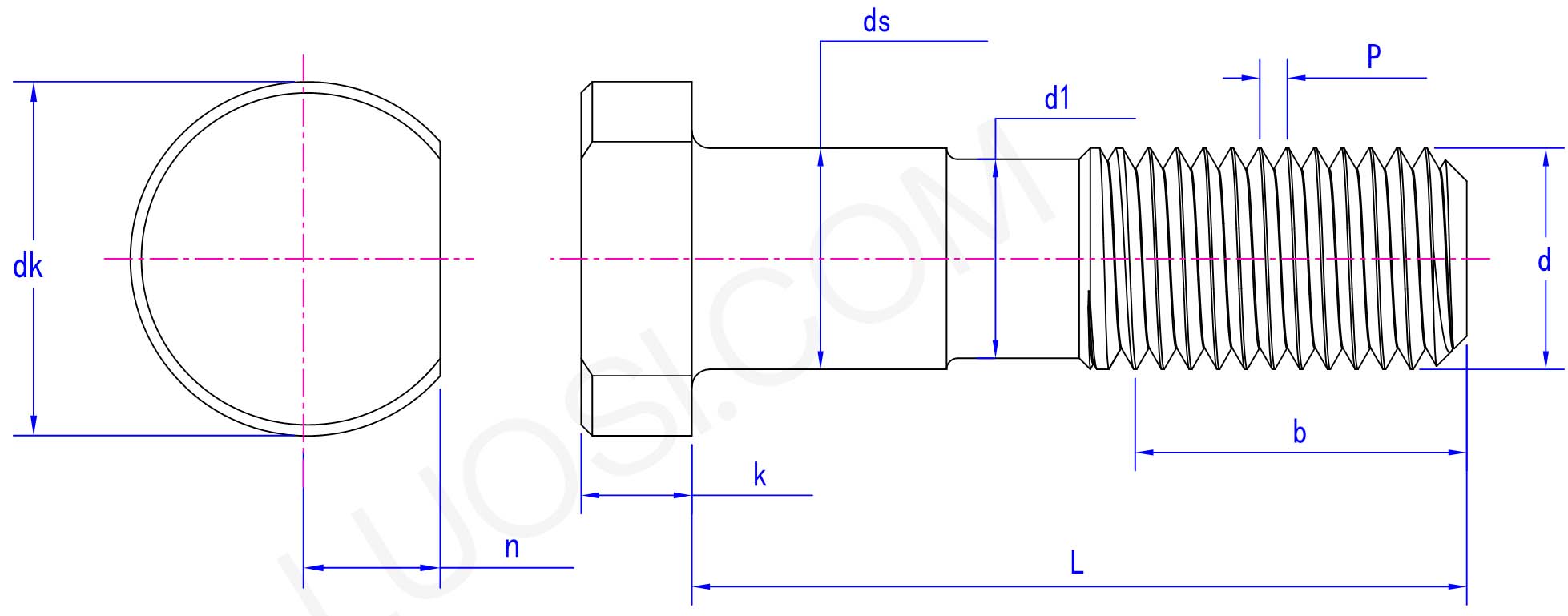
The top of the wheel hub bolt is an irregular circle, the rod body is cylindrical, and one end is machined with an external thread. There are a great many size specifications, with differences in thickness and length. You need to choose the appropriate bolts according to different vehicle models.
Product Features
The wheel bolt is a component that physically connects the wheel to the hub. They are screwed into the threaded holes of the hub assembly. When the bolts are tightened, they will firmly clamp the wheels in the hub. It is crucial to install these bolts correctly as they bear all the forces between the wheels and the vehicle during driving.
There is a conical seat beneath the head of the wheel hub bolt. This matches the conical holes on the rim. After being tightened, the conical seat precisely positions the wheel at the center of the hub and forms a tight and firm fit. It also helps to transfer the clamping force evenly. It is unsafe to use the wrong seat type (for example, spherical seat and conical seat).
The wheel bolt is a safety-critical fastener. Bolt damage may cause the wheels to fall off during driving, resulting in disastrous consequences. Therefore, the correct installation torque, the use of intact bolts, and regular inspections (such as after tire replacement) are of vital importance. They actually support your wheels.
Wheel hub bolts are highly resistant to pressure.When driving, the wheels have to bear the weight of the vehicle. During acceleration, braking and turning, they are also subjected to various forces. It needs to be strong enough to tightly connect the wheel and the hub together, preventing the wheel from loosening or falling off.
Product Parameters
| Mon | M10 | M12 | M14 | M16 | M20 | M22 |
| P | 1.25 | 1.25 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 |
| d1 | 9 | 11 | 13 | 15 | 19 | 21 |
| ds | 10 | 12 | 14 | 16 | 20 | 22 |
| dk | 18 | 18 | 22 | 28 | 32 | 36 |
| n | 6 | 7 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 14 |
| k | 4 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 10 | 10 |